Have you experienced the frustration of repeatedly asking Chat GPT or Bard or MidJourney (etc.) a relatively simple thing, and not getting the results you were looking for? You are not alone! As Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly language models like ChatGPT, have started to carve out a niche and offer immense potential, they come with their unique challenges, one of which is how to work efficiently with them.
Prompt engineering is the art and science of crafting effective inputs to guide an AI model towards generating the desired output.
In less fancy terms: prompts are our inputs, and the better we get at giving great prompts, the better the output will be. Although plugins like Prompt Perfect can help you, they still won’t do your job, so don’t rely solely on them.
Using ChatGPT and similar tools indeed has its risks: it may generate its answer from hallucinated sources or fails to provide sources altogether, and in most cases, the onus falls upon us, users, to verify the information – just to name a few. Despite its limitations, it is quickly becoming a must-have ally, which brings us to the crux of the matter – how do we ask the right questions?
Understanding the art of ‘prompt engineering’ is becoming increasingly critical. It’s so fundamental that I would make sure it is momentarily becoming part of the medical curriculum and recommend every medical professional to learn it. It will also be very soon part of our AI course. But while formal education can be an excellent starting point, there are practical tips and tricks to improve your prompt engineering skills in the meantime.
Like any skill, mastery of prompt engineering comes with practice. To save you some of the time and trial-and-error, here is what I’ve learned during the past months when I spent hundreds of hours refining my own approach. I now use these daily and I’m keen to share them with you.
Whether you’re a seasoned user of AI or just starting to dip your toes into this brave new world, these guidelines should make your journey smoother and more rewarding.
1. Be as specific as possible
The more specific your prompt, the more accurate and focused the response is likely to be.
Example:
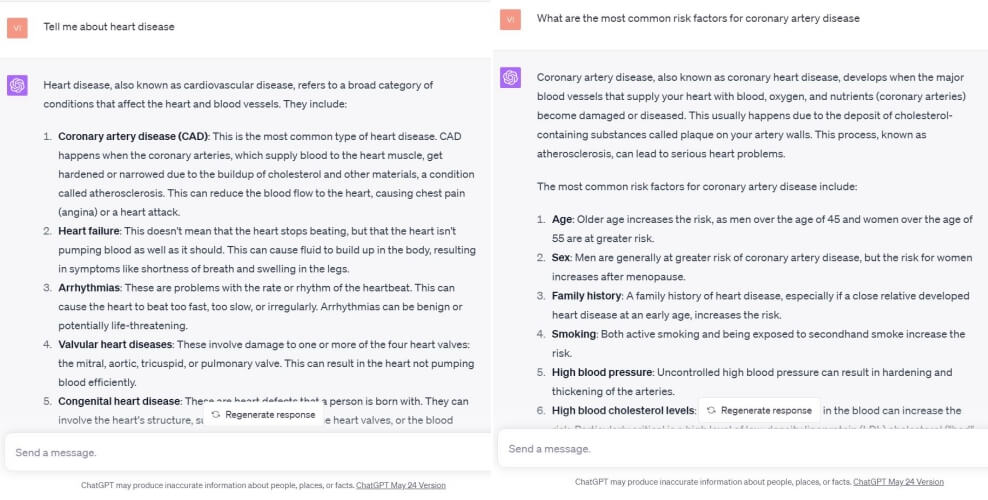
Less specific: “Tell me about heart disease.”
More specific: “What are the most common risk factors for coronary artery disease?”
2. Describe your goal
Describe exactly what kind of output you are looking for. It also helps highlight what’s important for you about the output.
Example: “I’d like to get a short list of 5 ideas for a Youtube video on the future of healthcare AI.”
3. Describe your setting and provide the context
Consider the discussion you are having with ChatGPT as a discussion you would have with a person you just met who might still be able to answer your questions and address your challenges. The better you describe your goal, your target audience, and the tone you would like to use, the more fitting the output will be.
Example:
“I’m writing an article about tips and tricks for ChatGPT prompt engineering for people working in healthcare. Can you please list a few of those tips and tricks with some specific prompt examples? My audience consists of medical professionals who are not AI experts. Please use a friendly, approachable tone.”
4. Experiment with different prompt styles
The style of your prompt can significantly impact the answer. Try different formats like asking to generate a list, provide a summary, or explain like I’m five (ELI5), etc.
Example:
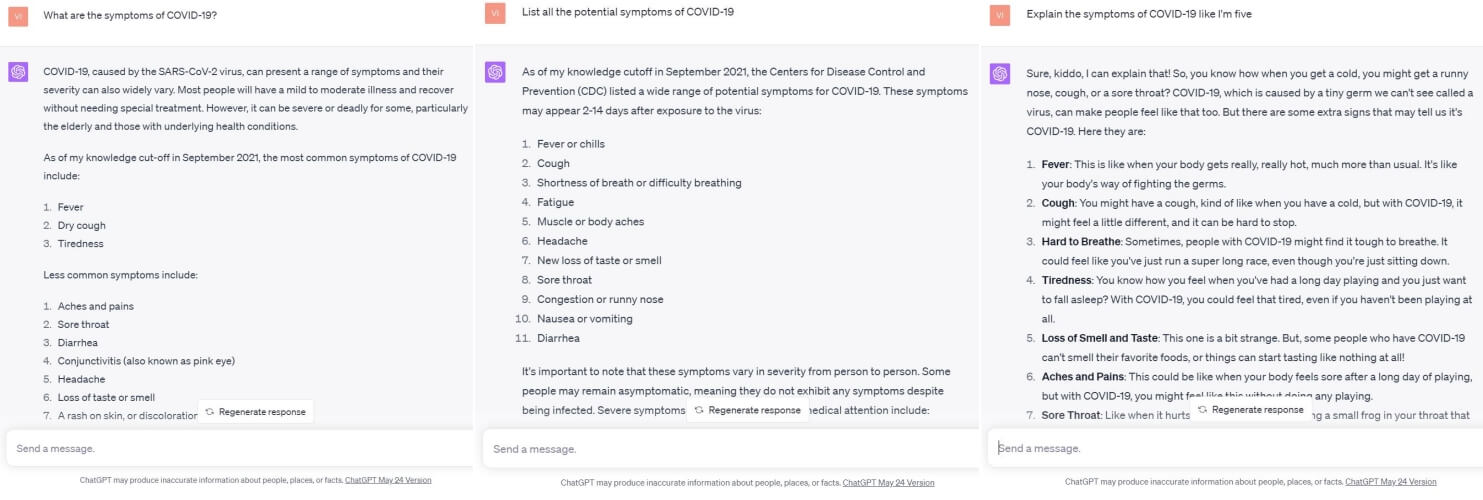
Direct Question: “What are the symptoms of COVID-19?”
Request for List: “List all the potential symptoms of COVID-19.”
Request for Summary: “Summarize the key symptoms and progression of COVID-19.”
ELI5: “Explain the symptoms of COVID-19 like I’m five.”
5. Ask it to play roles
This way, you can get the desired process of getting the information or input you were looking for.
Example:
“Act as a Data Scientist and explain Prompt Engineering to a physician.”
“Act as my nutritionist and give me tips about a balanced Mediterranean diet.”
6. Iterate and refine to delve deeper and/or get better answers
Unless you are simply amazing at prompt engineering, you rarely get the best response you were looking for after the first prompt. So feel free to refine your question. You are also encouraged to ask it to modify the output based on its previous response. If you’re not getting the output you want, try guiding the model with continuation prompts. This can be more effective than trying to get the perfect response in a single prompt. You can also make your prompt a conversation: ask the AI to think step by step or to debate the pros and cons before settling on an answer.
You: “What causes diabetes?”
AI: “Diabetes is primarily caused by the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin…”
You (refining the question): “What factors lead to the body’s inability to produce insulin?”
AI: “The body’s inability to produce insulin can be caused by autoimmune destruction of the beta cells in the pancreas, as in Type 1 diabetes…”
If you are moving into unknown territory and looking for information in a field you are not familiar with, you can use feedback loops to get into the details. While ChatGPT at first tends to provide very generic answers, you can always use its output as input for subsequent prompts.
Example:
You: “What are the common symptoms of Lyme disease?”
AI: “Common symptoms of Lyme disease can include fever, fatigue, headache, muscle and joint aches, and swollen lymph nodes.”
You: “What are the treatment options when these symptoms are confirmed to be due to Lyme disease?”
AI: “Lyme disease is typically treated with antibiotics…”

7. Use your previous threads
You can easily go back to a specific discussion by clicking on the right thread in the left column. This way, you don’t have to start all over again but can just continue a discussion you already had with ChatGPT.
8. Ask open-ended questions
Open-ended questions often yield more comprehensive responses.
Example:
Closed question: “Is exercise important for patients with osteoporosis?”
Open question: “How does regular physical activity benefit patients with osteoporosis?”
9. Request Examples
If there is something you are not satisfied with or don’t understand based on its response, first of all, tell ChatGPT that you don’t understand the answer and ask it to provide an example.
10. Use time wisely
If you’re asking about a process or timeline, specify that in your prompt.
Example:
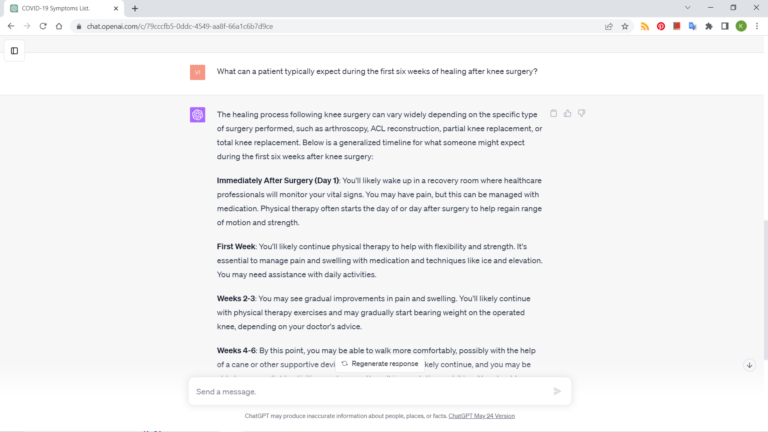
Without time reference: “Describe the healing process after knee surgery.”
With time reference: “What can a patient typically expect during the first six weeks of healing after knee surgery?”
+1. Set realistic expectations
Although GPT-4 is a powerful tool, it has its limitations. For instance, it can’t access real-time data (although you can already tweak this with plugins), it has a cutoff date of 2021 (which might not be a problem soon), and it doesn’t provide personal medical advice, or replace a professional’s judgment.
Example:
Unrealistic Prompt: “What’s the latest research published this month about Alzheimer’s?”
Realistic Prompt: “What were some of the major research breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s treatment up until 2021?”
In conclusion, as AI continues to grow and evolve, the importance of being adept at prompt engineering cannot be overstated. The ability to elicit useful and meaningful responses from AI can empower us to make the most of this cutting-edge technology. Remember, practice is key, and each question we ask is a step towards becoming more fluent in the language of AI.
In general, use it to expand your knowledge and ideas instead of solving things on behalf of you.
The post Prompt Engineering For Healthcare: 11 Tips To Craft Great ChatGPT Prompts appeared first on The Medical Futurist.